5 Spheres Of The Earth
The Four Spheres Of The Earth
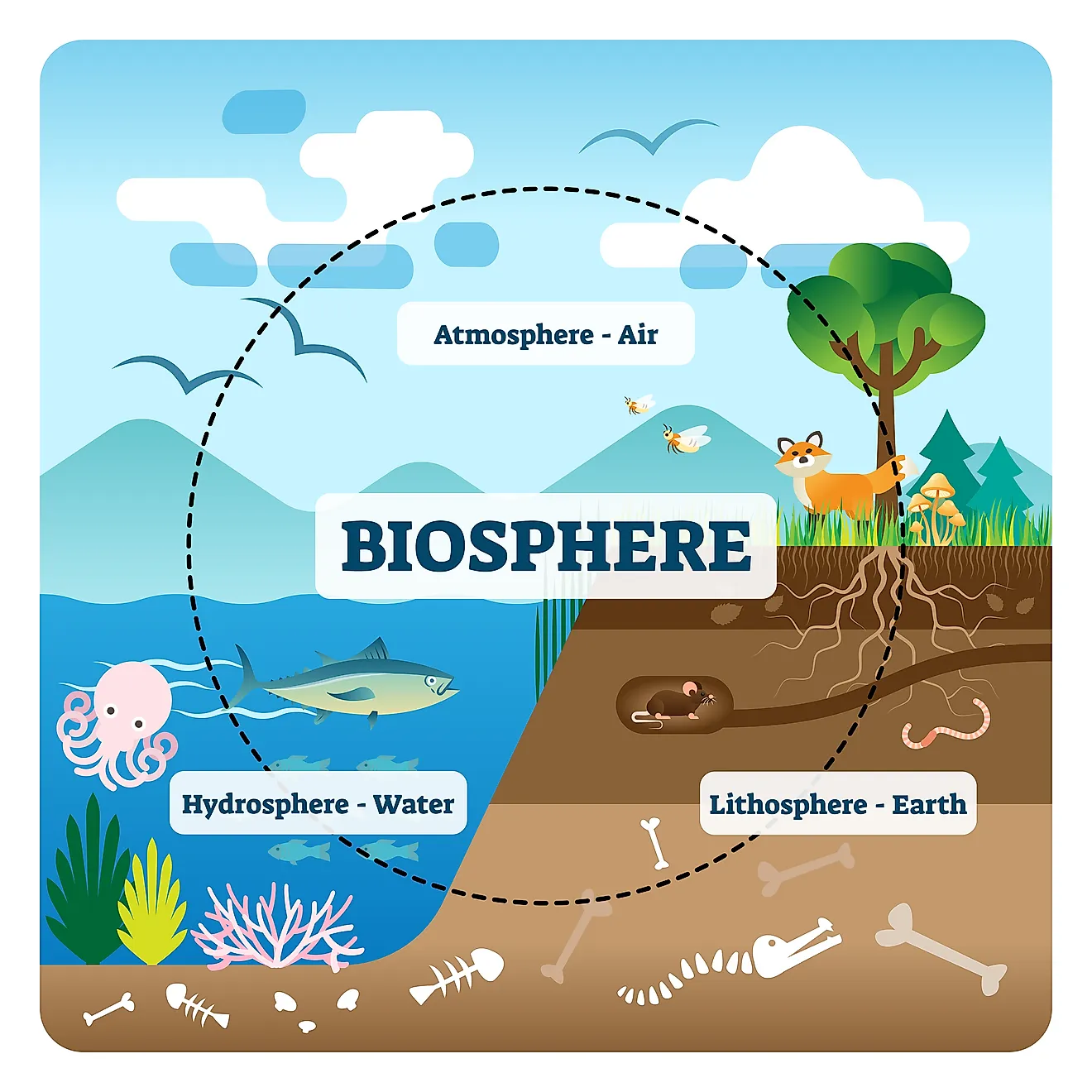
- The 4 spheres of the Earth are: the lithosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and temper
- The biosphere includes all living life on World: brute, plant, fungi, protist and monera
- All iv spheres must work in harmony to permit for the residuum of life to succeed of Earth. Any threat to one sphere, will have drastic effects on the others.
The earth tin be split into i of four major subsystems, namely: land, water, air, and all living things. These categories are known equally spheres, and are the lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere and biosphere, respectively. The first iii of these spheres are abiotic, meaning they are not living things, while the fourth - the biosphere - contains all biotic, or living creatures and organisms (everything from plants, to animals, to leaner).
Atmosphere

The atmosphere of World, which we casually refer to as simply 'air', is really made up of a mixture of gases and vapours. The Globe'due south atmosphere forms a barrier, or bubble around the Earth, and is held at that place by the force of gravity. This keeps the vapours of the atmosphere from escaping into outer space. Information technology is too this atmosphere which makes the earth inhabitable. The combination of chemicals in the air, likewise as the mode in which the atmosphere creates a bulwark between the Earth and the harmful rays of the sun, makes an environs in which animals, plants and man life can thrive.

The atmosphere can be separated and identified in several of its own layers, of which in that location are 5: the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere and exosphere. The Troposphere is the layer which holds the majority of the atmosphere, and is closest to the surface of the earth. This is besides the surface area in which well-nigh organic life lives, on Earth. The other layers extend outward from the surface, and are encompassed by the last layer, the Exosphere, earlier our atmosphere completely dissolves into Outer Space.
The temper of Earth is actually primarily made from nitrogen, with a limerick of 78 percent. The second most common gas in our atmosphere is Oxygen, which makes up 21%, and is the virtually important for both human and animate being life. The tertiary most prominent gas is argon, which is only 0.9 pct. This leaves the remaining 01. pct, which is classified as 'other' every bit no one gas is dominant enough to be significant. Nonetheless, this 'other' section does include water vapor, neon, carbon dioxide, and methane.
Hydrosphere
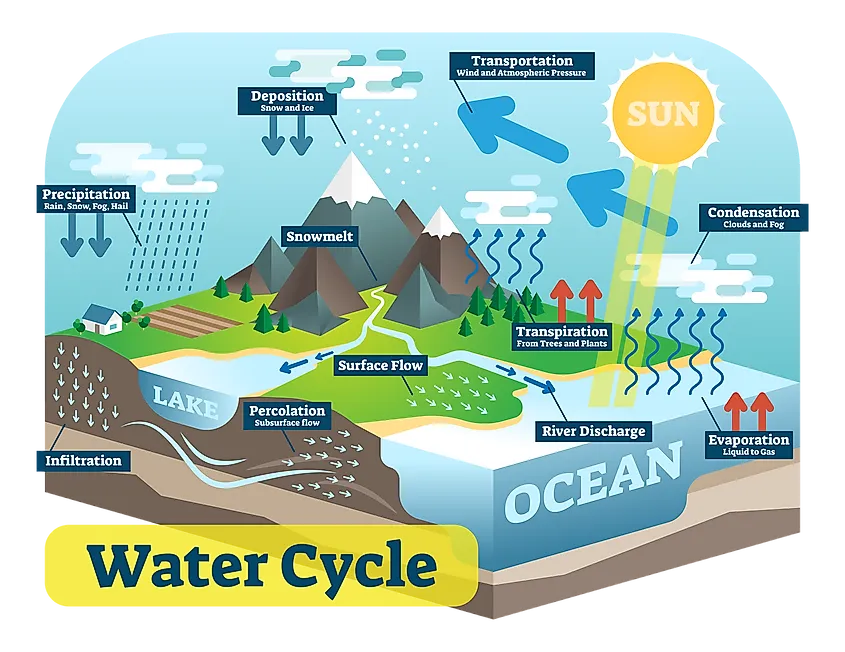
The hydrosphere is the water sphere of Earth. This includes the total amount of water that tin can be constitute on the whole planet, from that on the surface - like in lakes, oceans, rivers etc. besides equally water underground, and in the air. Considering it includes all water, this likewise means that it encompasses water that is found in liquid, vapor, or solid (ie ice) form.
Liquid

The first type of water most normally idea of, is liquid water. This tin be seen in a diversity of places and forms beyond the earth. Everything from lakes and seas, to streams, lagoons, rivers, creeks and springs are forms of liquid water which connect to form the hydrosphere. There is also an entire organisation of underground water that is besides in liquid class. This water is unremarkably accessed via aquifers, natural springs or wells. The surreptitious water organization is known as the h2o table, and contains all types of water that has go trapped below the surface. Groundwater fills the spaces betwixt sediment and rock, creating pockets of trapped water. Ofttimes, these pockets are tapped past humans via pipelines and wells, but in some cases the h2o naturally finds its style to the surface via springs and the like. This natural water source is also extremely useful for big found life like trees, that need considerably more water than that which they tin absorb through pelting and atmospheric moisture.
Vapor
H2o vapor, is any type of water that has evaporated, and now takes on a gaseous state. This includes things like fog and clouds. Water vapor forms an integral part of the water cycle. When liquid water evaporates, it turns into a gas, and becomes part of the atmosphere. Here, information technology can be redistributed into other parts of the globe. For example, a puddle - liquid - can be dried upwards in the sunday, forcing the h2o molecules to change and evaporate. Now, in gas grade, they form a cloud. This cloud is then diddled through the air, where it collects more moisture until the cloud becomes then heavy with water vapor that the vapor becomes liquid once again, falling back to the earth'south surface equally pelting.
Solid

Water in its solid form can be seen on globe equally water ice. This includes everything from the polar water ice caps, to frozen lakes and trophy, frost, snow, glaciers, and icebergs. This poly peptide of the hydrosphere can actually exist subsection into what is known every bit the cryosphere. While the cryosphere may not exist the first thing associated with water and the hydrosphere in general, it does play an important role in the larger system. It helps to regulate the global climate, and is home to a diversity of animals which rely on this frozen world to alive.
Lithosphere
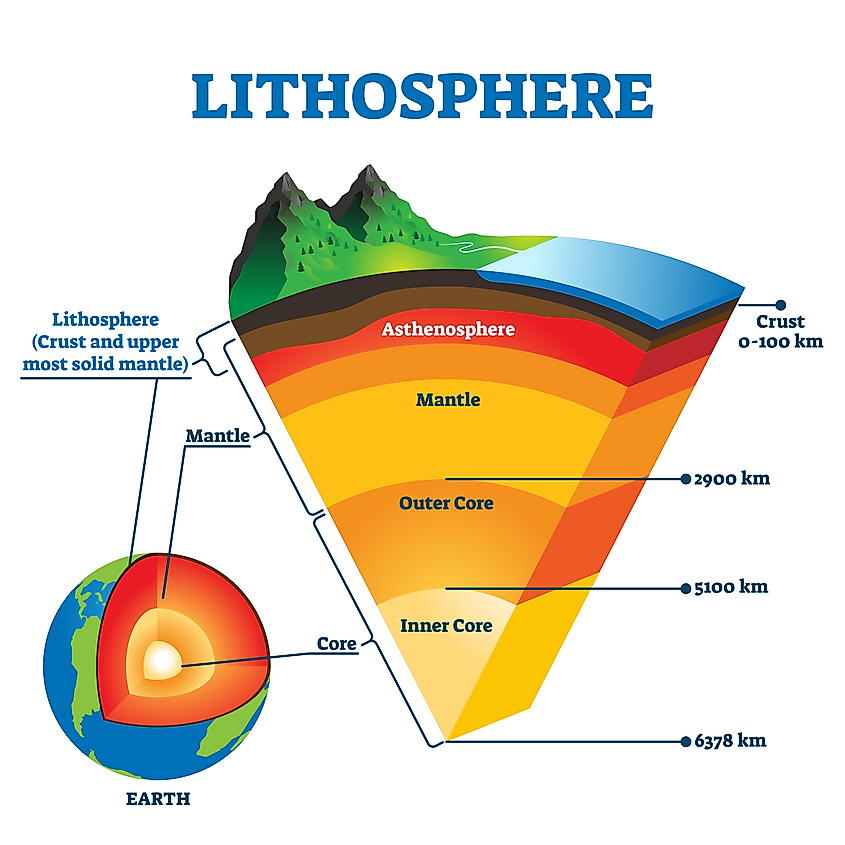
The lithosphere is the 'earth' or land portion of the Earth. It more specifically refers to the rocky outer surface of the Earth's chaff, and upper portion of the mantle. The Globe itself is dissever into several layers: the crust, upper and primary pall, the outer cadre and the inner core. Though all of this is Earth, it is only the more than solid upper portion that is included in the lithosphere. This means it is the generally solid, minimally viscous portion, every bit opposed to the more liquid molten lower layers. The lithosphere is the land on which biological life - i.eastward. the biosphere - exists.
Biosphere
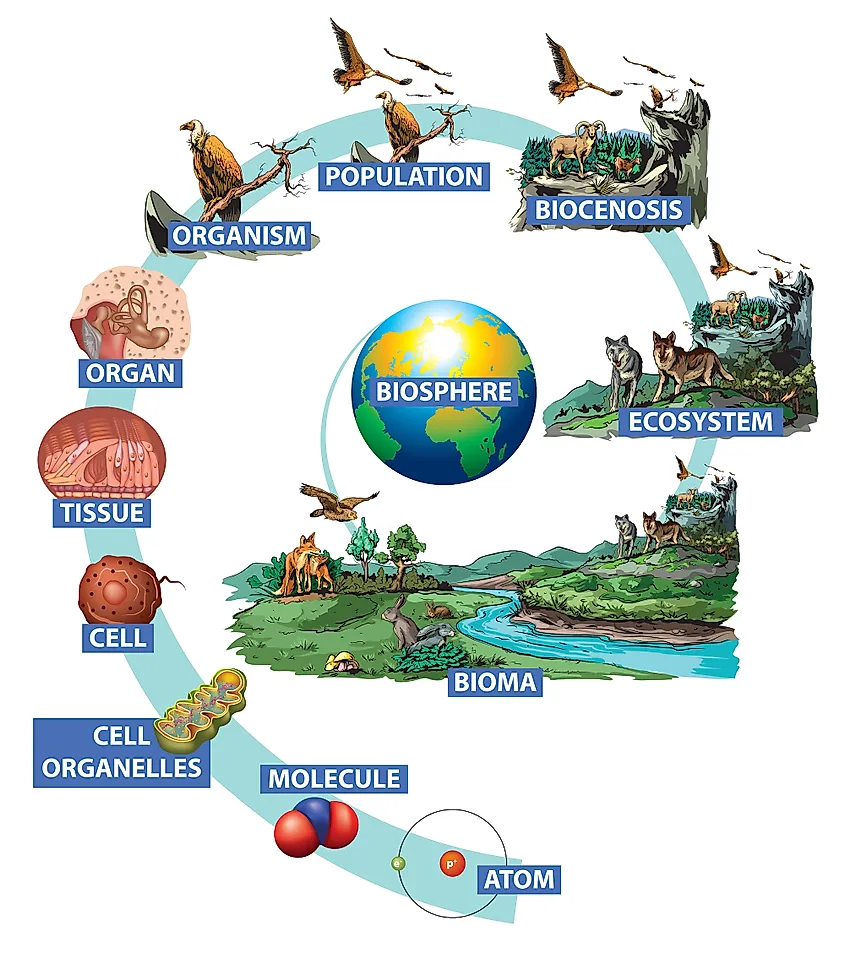
The biosphere is the sphere of the globe which includes all organic, living life. Whether this life is on the earth'south surface, in the atmosphere, or below the ground, it is function of the larger biosphere organization that makes upwards life on this planet. In this way, the biosphere blends with the other three spheres of Globe. The range of the biosphere is thought to be roughly 20 kilometers, or 12 miles from its highest signal, to its deepest. Generally speaking, though, most of the Earth'south life is much closer to the surface, and can exist found within about 500 meters or 1,640 feet beneath sea level, and half dozen kilometers, or 3.75 miles above the ocean'southward surface.
From the tallest mount to the deepest ocean, all organic life is part of the biosphere. This includes all types of life, from insects to fungi, animals and birds, plants and organisms like bacteria. This life is so divided into a serial of classifications: kingdoms, phylum, classes, orders, families, genus, and species. There are v unlike kingdoms, known as: animal, establish, fungi, protist and monera, and all of these cover the entirety of the biosphere. The large biosphere is then farther broken down into biomes and ecosystems, which are more specific working systems of animals and plants in any given area. Together, they form an intricate web of life which, when kept in balance, allows our Globe to run in harmony.
5 Spheres Of The Earth,
Source: https://www.worldatlas.com/geography/the-four-spheres-of-the-earth.html
Posted by: scottwhaption.blogspot.com


0 Response to "5 Spheres Of The Earth"
Post a Comment